What Marketing Jobs Are Available? A Comprehensive Guide
Marketing is an essential part of every business, large or small, and has evolved drastically in recent years. With the growing reliance on technology and digital platforms, the marketing industry now encompasses a wide range of roles, each crucial to helping companies succeed in an increasingly competitive landscape. From the traditional marketing roles to modern, digital-centric positions, the field of marketing is more diverse than ever before. Understanding the various types of marketing jobs and the skills required for each is key for anyone considering a career in this dynamic and evolving industry. Whether you are new to marketing or looking to switch roles, there’s a career path in marketing to suit your skills and interests.
In this article, we will explore several key marketing jobs, their responsibilities, and the skills required to succeed in each role. By understanding the types of positions available, you’ll gain insight into how you can pursue a rewarding and successful career in the marketing industry.
Digital Marketing Specialist
Digital marketing has emerged as one of the most critical and high-demand career fields in the modern marketing landscape. The role of a digital marketing specialist is to create and manage online marketing campaigns aimed at increasing a brand’s visibility and driving traffic to its website. This is a broad and versatile role that incorporates several aspects of digital marketing, including search engine optimization (SEO), social media marketing, email marketing, and online advertising.
A digital marketing specialist’s responsibilities may include developing and executing strategies for paid media campaigns, creating content for various digital platforms, managing social media accounts, and analyzing digital performance data to adjust and improve campaigns over time. They may also work closely with other teams, including content creators, designers, and developers, to ensure all online marketing efforts are aligned with the company’s overall marketing strategy.
To excel as a digital marketing specialist, individuals need a solid understanding of online marketing channels, analytics tools, and digital advertising platforms like Google Ads, Facebook Ads, and more. The ability to measure campaign performance and make data-driven decisions is essential in this role. Creative thinking and strong problem-solving skills are also necessary, as digital marketing is fast-paced and ever-changing.
Content Marketing Manager
In today’s digital age, content is king. As businesses increasingly rely on content to engage their audiences and drive conversions, the role of the content marketing manager has become more prominent. Content marketing managers are responsible for creating, curating, and managing content that aligns with a brand’s goals and speaks to the target audience.
This role typically involves overseeing content creation for blogs, websites, social media, email newsletters, and other digital platforms. A content marketing manager will develop content calendars, write and edit articles, collaborate with graphic designers and videographers, and ensure that all content is optimized for SEO. They may also be tasked with measuring content performance, using analytics tools to identify what works and what doesn’t, and adjusting strategies accordingly.
A successful content marketing manager needs to possess strong writing and editing skills, an understanding of SEO best practices, and the ability to develop content strategies that align with business objectives. Creativity is crucial in this role, as content must be both engaging and informative to attract and retain the audience’s attention.
SEO Specialist
Search engine optimization (SEO) is the practice of optimizing a website’s content to rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs). Given the critical importance of search visibility for businesses, the role of an SEO specialist has become indispensable. An SEO specialist’s job is to increase a company’s online presence and improve its rankings on search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo.
The responsibilities of an SEO specialist include conducting keyword research, analyzing competitors, optimizing on-page elements (such as meta tags, headings, and content), building backlinks, and improving technical SEO aspects like site speed and mobile-friendliness. Additionally, an SEO specialist must stay up to date with changes in search engine algorithms and SEO best practices to ensure ongoing success.
A deep understanding of search engine algorithms, data analysis, and content optimization strategies is essential for an SEO specialist. Proficiency in tools such as Google Analytics, Google Search Console, and keyword research platforms like SEMrush or Ahrefs is also highly beneficial. SEO specialists must be detail-oriented, analytical, and persistent in refining strategies to boost rankings and attract organic traffic.
Social Media Manager
With the rapid growth of social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and LinkedIn, the role of a social media manager has become increasingly important in modern marketing. Social media managers are responsible for developing and executing a company’s social media strategy, aiming to increase brand awareness, engage followers, and drive traffic to the business’s website.
Key responsibilities include creating social media content, scheduling posts, responding to customer inquiries and comments, and monitoring social media metrics. Social media managers also collaborate with marketing teams to ensure that social media campaigns align with broader marketing initiatives. Additionally, they analyze performance data to determine the success of campaigns and adjust strategies for maximum impact.
A social media manager must have a strong understanding of the platforms they work with, as well as the ability to create engaging content that resonates with their audience. Knowledge of social media advertising, analytics tools, and trends is also essential for success in this role.
Email Marketing Specialist
Despite the rise of social media and other digital marketing channels, email marketing remains one of the most effective ways to engage with customers and drive conversions. An email marketing specialist focuses on creating and managing email campaigns designed to reach customers with personalized, relevant content.
Responsibilities of an email marketing specialist include designing email templates, segmenting email lists, crafting compelling copy, and analyzing email performance metrics like open rates, click-through rates, and conversions. The goal is to build relationships with customers through regular communication, using automation tools to send targeted messages based on user behavior and preferences.
To be successful as an email marketing specialist, individuals need strong writing skills, knowledge of email marketing platforms (such as Mailchimp, Constant Contact, or HubSpot), and the ability to analyze data to continuously improve campaign effectiveness. Understanding customer segmentation and personalization is also crucial for increasing engagement and achieving higher conversion rates.
PPC (Pay-Per-Click) Manager
The role of a PPC manager involves overseeing paid advertising campaigns on search engines (such as Google Ads) and social media platforms (like Facebook Ads). PPC campaigns are designed to drive targeted traffic to a website in exchange for a fee each time someone clicks on an ad. As a PPC manager, you will be responsible for developing paid search strategies, creating ads, managing budgets, and optimizing campaigns to achieve the best return on investment (ROI).
PPC managers typically work with tools like Google Ads, Bing Ads, and Facebook Ads Manager to create and optimize campaigns. They must also analyze performance metrics, such as click-through rates, conversion rates, and cost-per-click, to refine strategies and improve the overall effectiveness of paid campaigns.
To succeed in PPC management, you need a strong understanding of online advertising platforms, analytical skills to interpret data, and the ability to optimize campaigns for maximum performance. It also requires creativity in crafting ads that will capture the attention of potential customers and drive conversions.
Marketing Analyst
A marketing analyst is responsible for collecting and analyzing data to assess the effectiveness of marketing campaigns and inform future decision-making. Marketing analysts work closely with other marketing professionals to gather insights about customer behavior, market trends, and competitor strategies.
In this role, analysts utilize various tools to track the success of marketing initiatives, such as website traffic, conversion rates, social media engagement, and email performance. They then compile and interpret this data to provide actionable insights that help improve marketing strategies and achieve business goals.
Marketing analysts must be detail-oriented, possess strong analytical skills, and be comfortable working with tools like Excel, Google Analytics, and data visualization software. The ability to interpret data and communicate findings effectively is key in this role, as the insights provided by marketing analysts can have a significant impact on business strategy.
Brand Manager
A brand manager is responsible for developing and maintaining a brand’s image, identity, and overall strategy. Brand managers ensure that all marketing efforts, from advertising to product development, align with the company’s brand values and goals. They often work closely with other departments, including product development, sales, and marketing, to ensure brand consistency across all touchpoints.
Key responsibilities include conducting market research, analyzing consumer behavior, and developing campaigns to strengthen the brand’s presence. Brand managers also oversee product launches, marketing communication strategies, and collaborations with external partners or influencers.
Brand managers must have strong communication and leadership skills, as they frequently collaborate with cross-functional teams. A deep understanding of market trends and consumer behavior is also essential, as brand managers must ensure their brand remains relevant and appealing to the target audience.
Public Relations (PR) Specialist
A public relations (PR) specialist is responsible for managing a company’s image and handling media relations. PR specialists work to maintain a positive public perception of their brand by crafting press releases, managing media inquiries, and building relationships with journalists and media outlets. They also play a key role in crisis management, helping to protect the company’s reputation during challenging situations.
PR specialists also work closely with other departments, including marketing and communications, to ensure consistent messaging across all channels. A successful PR specialist must have excellent writing skills, a strong network of media contacts, and the ability to think strategically under pressure.
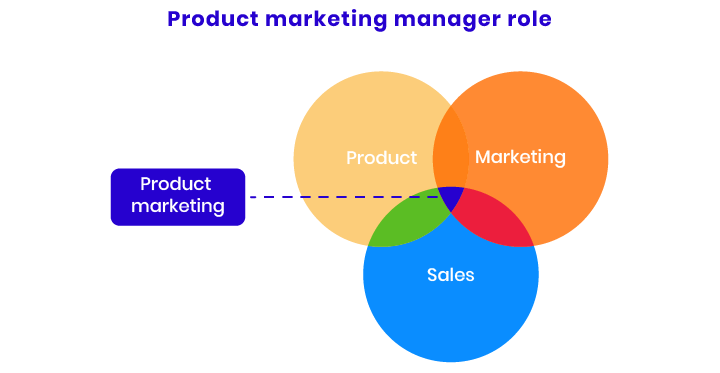
Product Marketing Manager
A product marketing manager is responsible for positioning a product in the market, developing go-to-market strategies, and ensuring the product meets the needs of its target audience. This role involves collaborating with various departments, including product development, sales, and marketing, to align product offerings with customer expectations and market trends.
Product marketing managers are tasked with creating product messaging, identifying target audiences, and developing campaigns to drive demand. They also gather feedback from customers and stakeholders to inform product improvements and ensure the product’s success in the market.
To excel as a product marketing manager, individuals need strong project management skills, a deep understanding of the product development process, and the ability to analyze customer feedback and market trends.
Conclusion
The marketing field offers a vast array of career opportunities, ranging from digital marketing roles to traditional positions in public relations, brand management, and product marketing. With the constant evolution of digital platforms and marketing strategies, professionals in this industry need to stay adaptable and continue learning. Whether you’re interested in data-driven roles like marketing analytics or creative positions like content creation, there’s a marketing career path that can align with your skills and interests. By understanding the diverse job roles and their requirements, you can make an informed decision about which career path to pursue in the marketing industry. As businesses increasingly invest in marketing to stay competitive, the demand for skilled marketing professionals will continue to grow, providing exciting opportunities for those entering the field.